

Project Overview
案例概述
Time: April 2023 to present
Location: Yinzhou No.2 Experimental Middle School, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, China
Main Contents:
1. Curriculum Integration: Offered compulsory STEAM courses and carried out community composting practices.
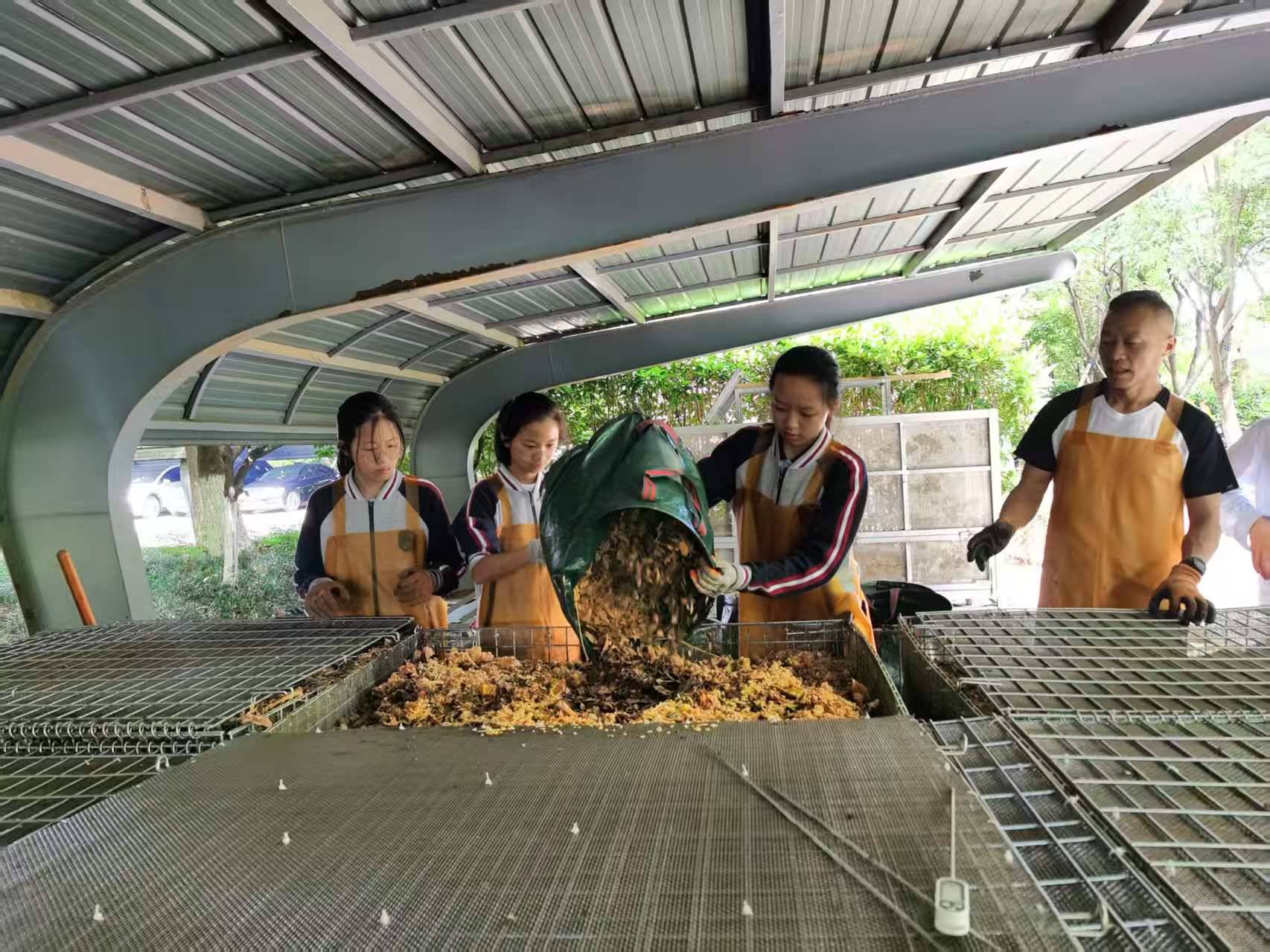
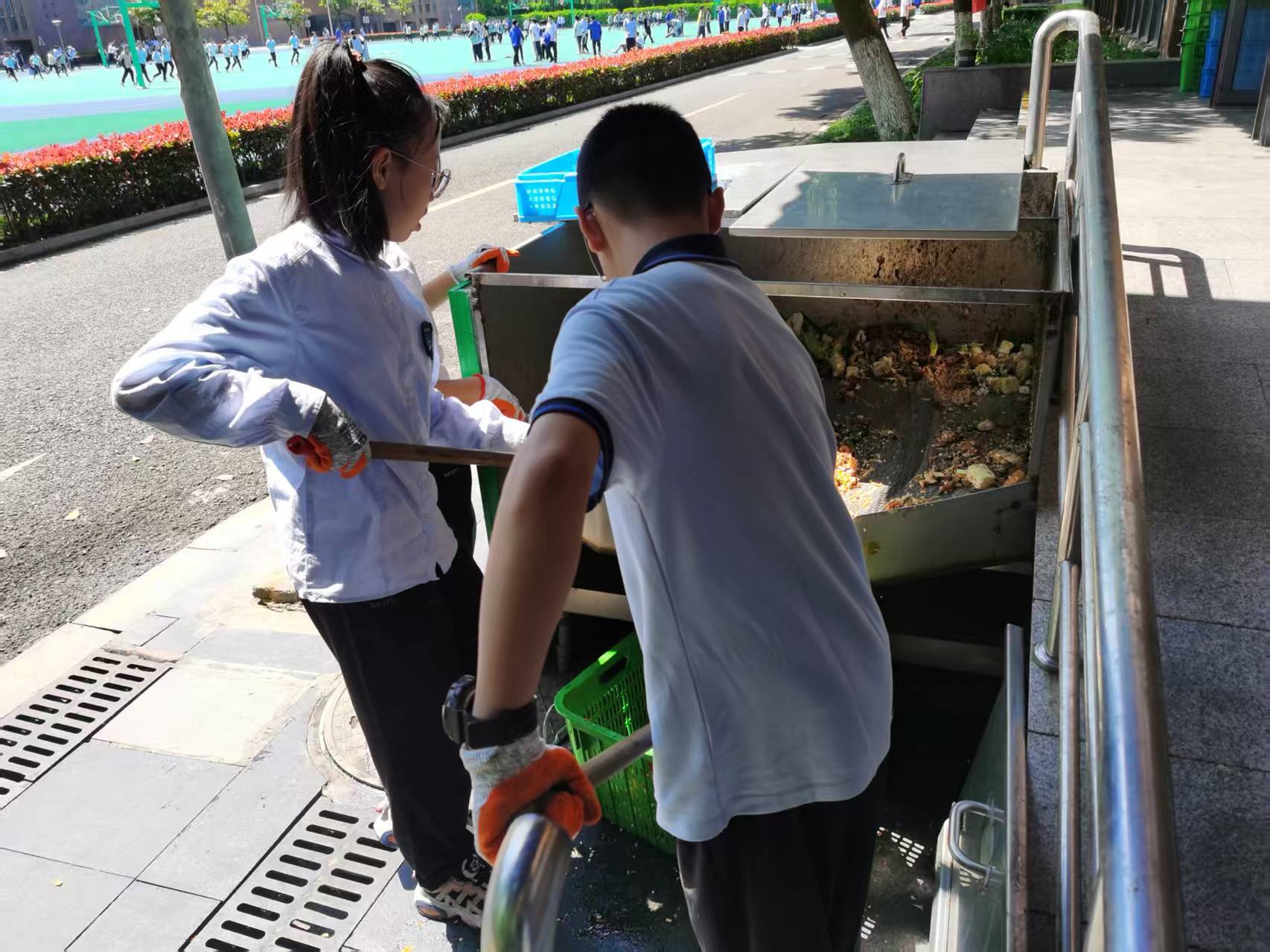
2. Resource Recycling: Collected pre- and post-meal kitchen waste and garden waste on campus, converted them into organic fertilizer through composting, and established a "waste-resource" closed-loop system.
3. Team Collaboration: Led by the principal and managed by the General Affairs Office, it involved personnel from logistics, gardening, kitchen, and property management, forming a cross-departmental collaboration mechanism.
4. Professional Empowerment: Teacher Gu Lingyun joined the "Community Kitchen Waste Composting Platform Composter" program in 2024 and obtained the Composter Certificate and a scholarship in 2025, promoting the professionalization of teaching.
Project Achievements:
1. On-campus Results: 100% of pre- and post-meal kitchen waste was composted on campus, and our school was recognized as an advanced school in garbage classification in Ningbo City.
2. Academic Transformation: The school-based composting course "Zero Waste Campus Construction - Kitchen Waste" was rated as a 3-star case by the "Zhejiang Provincial Education Research Institute" and was selected into the excellent case library of the "Curriculum and Textbook Research and Development Center of the Chinese Academy of Educational Sciences".
3. Regional Radiation: The experience was promoted to all communities in Xiaying Street, Yinzhou District, contributing to the achievement of the "low-carbon goal".
4. Social Impact: Through the community kitchen waste composting platform, it exchanged experiences with peers across the country, became a model for garbage classification education, and gained industry recognition.
时间:2023年4月至今
地点:中国浙江省宁波市鄞州第二实验中学
主要内容:
1. 课程融合:开设必修STEAM课程,开展社区堆肥实践。
2. 资源循环:回收校内餐前和餐后厨余、园林垃圾,通过堆肥转化为有机肥,构建“垃圾-资源”闭环系统。
3. 团队协作:校长牵头,总务处主导,联动后勤、园林、厨房、物业人员,形成跨部门协作机制 。
4. 专业赋能:顾凌云老师2024年加入“社区厨余堆肥平台堆肥师”计划,2025年获得堆肥师证书同时获得奖学金,推动了教学专业化。
项目成果:
1. 校内成效:餐前餐后厨余垃圾100%进行堆肥,我校被评为宁波市垃圾分类先进学校。
2. 学术转化:校本堆肥课程《校园零垃圾建设之厨余垃圾》的案例被“浙江省教研室”评为最高等级3星级案例,被“中国教育科学研究院课程教材研发中心”入选优秀案例库。
3. 区域辐射:经验推广到鄞州区下应街道各个社区,助力“低碳目标”达成。
4. 社会影响:通过社区厨余堆肥平台与全国同行交流,成为垃圾分类教育范本,获行业认可。

Company/Organization Profile
机构简介
Yinzhou No.2 Experimental Middle School**, located at No. 591, Xiaying South Road, Yinzhou District, Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province, China, traces its origins to the junior high school division of Yinzhou High School, a former provincial key high school in Zhejiang. In August 1998, it commenced independent operation as Ningbo Yinzhou Lanqing School, swiftly establishing itself as a top-tier junior high school within the greater Ningbo metropolitan area. In August 2022, the institution transitioned to a public school model, adopting its current name, Yinzhou No.2 Experimental Middle School, and embarking on a new chapter while continuing its legacy of educational excellence.
鄞州第二实验中学,位于中国浙江省宁波市鄞州区下应南路591号,前身是宁波市浙江省重点高中鄞州中学初中部,1998年8月以鄞州蓝青学校身份独立办学,成为宁波大市内首屈一指的优质初中。2022年8月,蓝青学校以鄞州第二实验中学公办学校身份开启新的办学旅程。继续以优秀的教学质量与科学规范的管理赢得社会的广泛认可。传承鄞州中学基因,秉持蓝青学校特质,以“青出于蓝”为校训,培养“具有科学精神、人文底蕴、独立个性和健康生活的优秀社会公民”,为高一级学校输送优质人才。

Project Outcome
项目成果
1. On-campus Impact: Implemented a “mandatory school-based STEAM curriculum” for all 425 Grade 7 students (2 class hours/week). Students initiated a "Zero-Waste Campus" proposal. Addressing waste reduction and precise classification needs, they launched community composting practices. 100% of pre- and post-meal kitchen waste, alongside daily garden waste (~100 kg), is composted on-site, processing 200 kg of food waste daily. Student involvement in composting and the introduction of portion-weighing technology achieved source reduction and precise waste sorting.
2. Academic Recognition: The school-developed composting course case study, "Kitchen Waste Management for a Zero-Waste Campus," was rated the highest-tier (3-star) case by the Zhejiang Provincial Institute of Education Research and selected for the National Exemplary Case Repository by the National Research Center for Curriculum and Textbook Development, Chinese Academy of Educational Sciences. This established an "Education + Technology" dual-driver model.
3. Regional Influence: Recognized as a "Ningbo Municipal Model School for Waste Classification."Project methodologies have been successfully replicatedacross communities in Xiaying Sub-district, Yinzhou District, contributing significantly to local carbon reduction goals
4. Societal Impact:Gained national recognition within the industry as a model for waste classification education. The project facilitates knowledge exchange through a community composting platform, engaging practitioners nationwide.
1. 校内成效:校本必修STEAM课程,初一425位学生每周2课时,学生提出“零垃圾学校建设”倡议,结合垃圾减量与精准分类需求,开展社区堆肥实践。把餐前餐后厨余垃圾100%进行堆肥,每天处理厨余垃圾约200斤,园林垃圾约100斤。学生参与堆肥和引入新科技(称量式打菜),实现了源头减量和精准分类
2. 学术转化:校本堆肥课程《校园零垃圾建设之厨余垃圾》的案例被“浙江省教研室”评为最高等级3星级案例,被“中国教育科学研究院课程教材研发中心”入选优秀案例库,探索“教育+技术”双驱动模式。
3. 区域辐射:我校被评为宁波市垃圾分类先进学校。 经验推广到鄞州区下应街道各个社区,助力“低碳目标”达成。
4. 社会影响:通过社区厨余堆肥平台与全国同行交流,成为垃圾分类教育范本,获行业认可。

Project Highlights
项目亮点
I. Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration: Under the principal's leadership, we established cross-departmental collaboration involving the General Affairs Office, Logistics, Kitchen/Catering Services, and Property Management.
II. Resource Circulation: We transformed pre- and post-consumer kitchen waste and garden trimmings into valuable resources, achieving **100% resource recovery rate** for organic waste on campus.
III. Curriculum Integration: We combined classroom instruction with hands-on composting activities, enhancing students' theoretical knowledge and practical skills simultaneously.
IV. Experience Dissemination:We scaled our successful "Zero-Waste Campus" model, promoting it to district, municipal, and rural communities to advance ecological civilization.
一、多方协同:校长支持下,联动总务处、后勤、厨房及物业,构建跨部门协作二、资源循环:将餐前餐后厨余、园林垃圾变废为宝,实现校内有机废弃物100%资源化。
三、课程融合:集中授课与分散堆肥结合,学生理论实践同步提升。
四、经验辐射:从建设零垃圾学校,到向区、市及农村社区推广模式,助力生态文明建设。
Project Implementation
项目实施
I. Project Background & Objectives
- Timeline: curriculum launched in 2018; deep-dive implementation 2023-2025
- Location: our campus
Core targets
① Convert 100 % of cafeteria & landscaping waste into compost on site.
② Build a “Zero-Waste Demonstration School” and extend the model to the neighborhood.
③Create a replicable“education-practice-community linkage” template.
II. Implementation Plan & Process
Stage 1 – Tackling three bottlenecks (2023-2024)
Challenge | Counter-measure | Supporting party
Funding gap | Donations from caring individuals | Caring individuals
Staff shortage | Head of general affairs leads, student volunteers recruited, rotating shifts during long break | —
Limited spare time | Centralized theory lessons + distributed practice, credits awarded | —
Stage 2 – Key technology roll-out & enablement
1. Technical support
- Nanjing University Lishui Institute supplies composting technology and product testing.
- Jianling Village, Fenghua, shares rural composting experience to refine compost bins.
2. Process optimization
(1) Drain cafeteria waste to cut salt content.
(2) Shred landscaping branches and mix with food scraps.
Stage 3 – Cross-district scaling (from 2025)
- Co-build a Community Compost Education Station with Xiaying Sub-district; train residents.
- Nanjing University Lishui Institute provides data-monitoring support.
III. Before-vs-After Analysis
Indicator | Pre-implementation | Post-implementation
Daily food-waste handling | 0 kg | 300 kg (all composted)
Curriculum value | STEAM courses lacked hands-on carriers | School-based compost course created; 100 % student participation; awards in district & city contests
Community linkage | No external partners | Xiaying Sub-district now running community composting
一、项目背景与目标
时间:2018年启动课程,2023-2025年深化实践
地点:本校
核心目标:
① 校内实现餐厨/园林垃圾100%堆肥资源化。
② 建成“零垃圾示范校”并向社区推广。
③ 形成可复制的“教育-实践-社区联动”模式。
二、实施方案与过程
阶段1:攻坚三大核心挑战(2023-2024年)
挑战 | 应对策略 | 支持方 |
资金短缺 | 热心人士捐助 | 热心人士 |
人手不足 | 总务主任牵头,招募学生志愿者,大课间轮岗 |
|
课余时间紧张 | 集中授课传理论+分散实践,纳入课程学分激励, |
|
阶段2:关键技术落地与赋能
1. 技术支持:
南京大学溧水研究院提供堆肥技术和堆肥产物的检测。
奉化箭岭村分享农村堆肥经验,改进堆肥箱。
2.流程优化:
(1)餐厨垃圾沥水减少含盐量。
(2)园林树枝叶粉碎与厨余混合。
阶段3:跨区域辐射推广(2025年起)
与下应街道共建社区堆肥教育站,培训社区居民堆肥技术。
南京大学溧水研究院提供数据监测支持。
三、实施前后对比分析
提升效果 | 实施前 | 实施后 |
垃圾处理 | 日均厨余垃圾0斤 | 日均厨余垃圾300斤 |
课程价值 | STEAM课程缺乏丰富的实践载体 | 开发校本堆肥课程,学生实操率达100%,学生获区市级实践比赛中获奖 |
社区联动 | 无外部合作 | 带动下应街道社区社区堆肥 |

Project Impact & Sustainability
项目影响力、可推广性与可持续性
I. Project Impact
Using a STEAM curriculum as its vehicle, the initiative delivers multiple dividends through the creation of a “Zero-Waste Campus”:
1. Environmental–100 % of cafeteria and landscaping waste is converted into resources on site, eliminating the need for landfill or incineration.
2. Educational – More than 1 000 students have developed a sense of ecological responsibility; the “centralized lessons + rotating hands-on duty” model has been added to the district’s STEAM best-practice library.
3. Social–Teacher Gu Lingyun presented at a national composting symposium and earned professional certification; project know-how is now being shared with Xiaying-sub-district neighborhoods through the Vanke Foundation platform.
II. Replicability
The project offers three advantages for rapid uptake:
- Low-cost & easy to run: it relies on existing campus space and cafeteria waste; no expensive equipment is required.
- Cross-scenario ready: proven “school + community” dual template already exists.
- Policy-aligned: it answers the national “Zero-Waste Cities” and rural-revitalization strategies, enjoys technical support from the Nanjing University Lishui Institute, and supplies standardized procedures that can be copied quickly.
III. Sustainability
- Institutional safeguard: a permanent management system led by the principal, executed by the general-affairs office, and coordinated across departments.
- Resource loop: compost products feed campus landscaping and nearby farmland, forming a circular chain of “waste → fertilizer → produce”.
- Capacity building: on-campus teachers earn “compost-master” certification; student clubs operate the project autonomously to ensure continuity.
Next step: expand university–enterprise cooperation, explore marketization of organic fertilizer, and secure a win-win in both ecological and economic returns.
一、项目影响力
该项目以STEAM课程为载体,通过“零垃圾学校”建设实现多重效益:
1. 环境层面,实现校内厨余与园林垃圾100%资源化减少填埋/焚烧污染;
2. 教育层面,培养超千名学生的生态责任感,其“集中授课+轮值实践”模式被纳入区域STEAM优秀案例库;
3. 社会层面,顾凌云老师参与国家级堆肥研讨会并获专业认证,项目经验通过万科公益基金会平台辐射下应街道社区。
二、可推广性
项目具备三大复制优势:
低成本易操作,利用现有校园场地与厨余资源,无需高额设备投入;
跨场景适配,已形成“学校-社区”双模式;
政策契合度高,响应国家“无废城市”与乡村振兴战略,获南京大学溧水研究院技术支持,标准化流程便于快速复制
三、可持续性
机制保障:建立校长牵头、总务处主责、跨部门协同的长效管理体系;
资源闭环:堆肥产品反哺校园绿化与周边农田,形成“废弃物-肥料-农产品”循环经济链;
能力建设:通过堆肥师认证培养校内专业师资,学生社团自主运营确保项目延续性。未来拟拓展校企合作,探索有机肥料市场化路径,实现生态效益与经济效益双赢。
(Using AI translation)
(使用AI翻译)

能源至净,生活至美,积极打造碳中和
10-24 · 来源:中国石化销售股份有限公司海南海口石油分公司 · 作者:中国石化销售股份有限公司海南海口石油分公司
无锡中瑞低碳生态城
10-23 · 来源:无锡中瑞低碳生态城 · 作者:无锡中瑞低碳生态城

南山云科技大厦零废弃实践成果——基于“空间改造-员工行动-客户延伸”三级落地模式
10-23 · 来源:深圳南山云科技大厦 · 作者:深圳南山云科技大厦