

Project Overview
案例概述
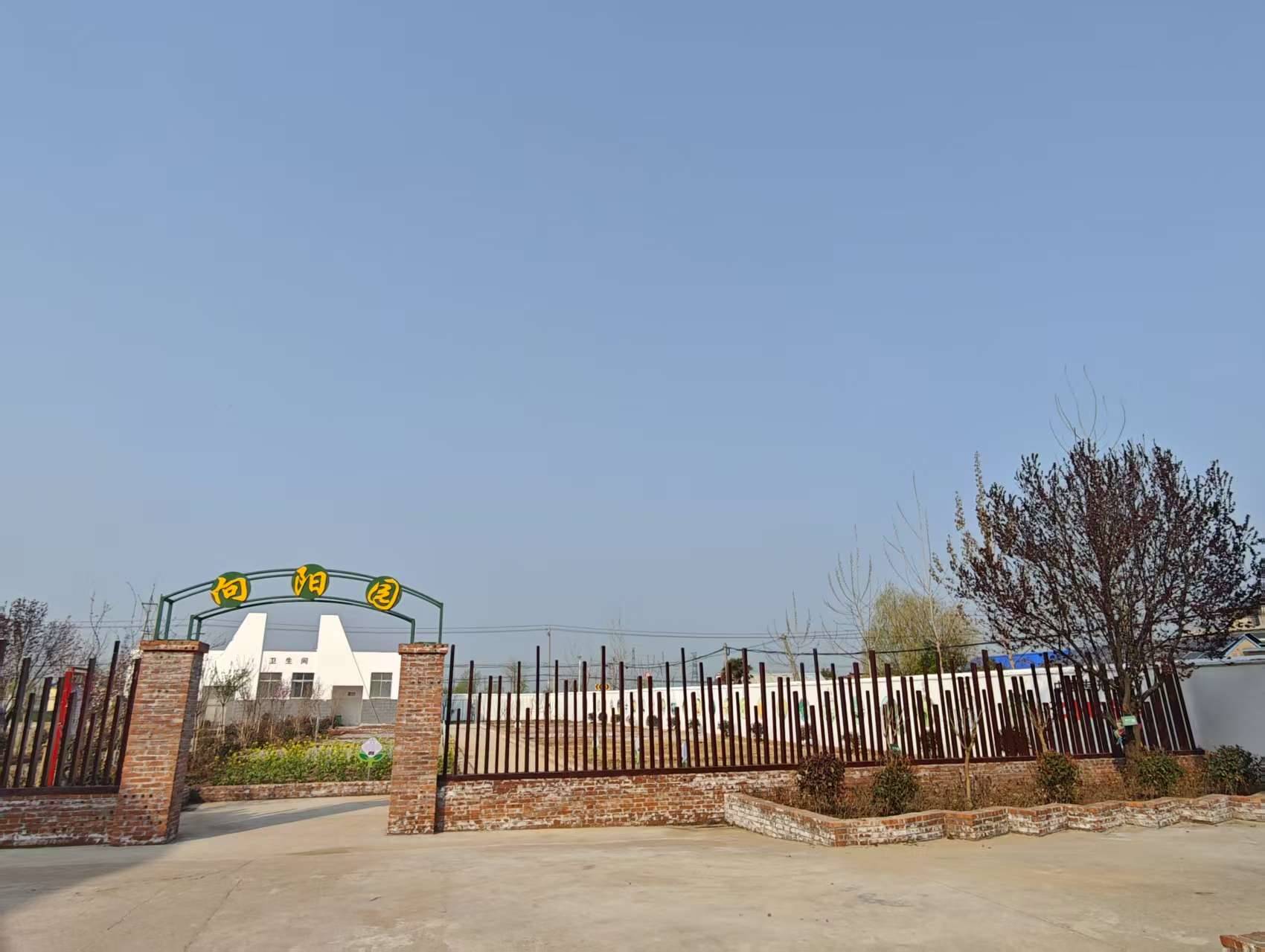
The Xiangyangyuan Labor Practice Base of Daquan Experimental School in Guannan County started construction in 2022 and is located in the core area of the school's biology curriculum base. Relying on the junior high school biology curriculum base, the project plans functional areas such as native plant planting area, ecological observation area, and organic cultivation area, equipped with ecological facilities like rainwater irrigation and organic fertilizer treatment, thus building an integrated green space of "teaching-practice-science popularization".
灌南县大圈实验学校向阳园劳动实践基地于 2022 年启动建设,位于该校生物课程基地核心区域。项目依托初中生物课程基地,规划本土植物种植区、生态观测区、有机培育区等功能区域,配备雨水灌溉、有机肥料处理等生态设施,构建 “教学 - 实践 - 科普” 一体化绿色空间。
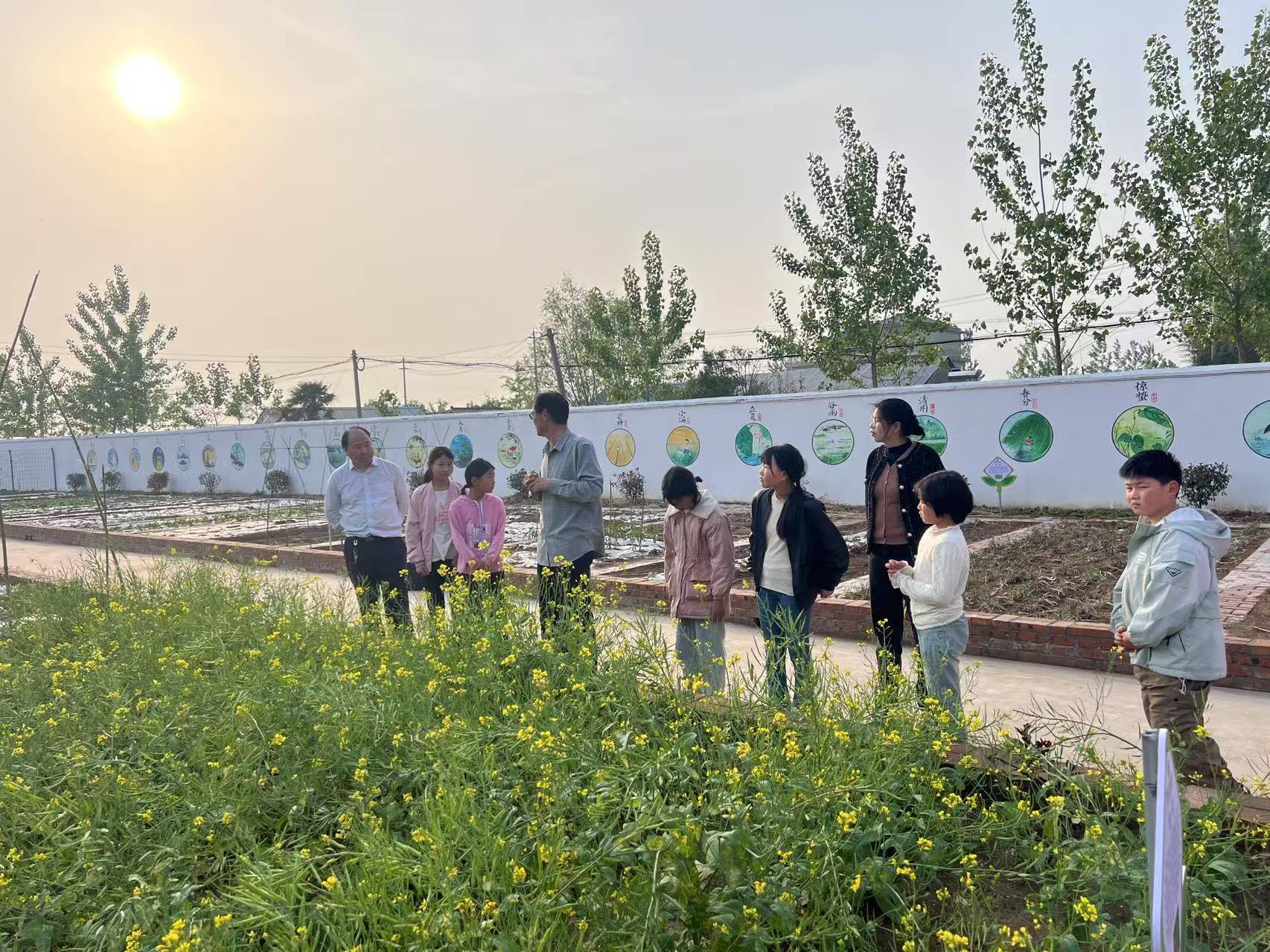

The base adopts a three-level management model of "school-led, teacher-responsible, and student-participated", carrying out regular teaching activities such as plant growth observation and organic planting practice, and regularly holding public participation activities including campus open days and environmental protection-themed lectures. It has established student ecological monitoring teams to record and analyze environmental data, promoting native plant protection and resource recycling.
基地采用 “学校主导、教师负责、学生参与” 的三级管理模式,开展植物生长观察、有机种植实践等常态化教学活动,定期举办校园开放日、环保主题宣讲等公众参与活动。建立学生生态监测队伍,记录分析环境数据,推动本土植物保护与资源循环利用。

Since the project's implementation, the base has achieved a vegetation coverage rate of over 90%, a rainwater utilization rate of more than 30%, and a significant annual reduction in garbage emissions. 92% of participating students have gained a direct understanding of the plant growth process, driving surrounding families to participate in green practices. Relevant activities have been repeatedly reported by county-level media, forming a replicable operation model for campus green spaces.
项目实施以来,基地植被覆盖率超 90%,雨水利用率达 30% 以上,年减少垃圾排放显著。92% 参与学生直观认识植物生长过程,带动周边家庭参与绿色实践,相关活动获县级媒体多次报道,形成可复制的校园绿色空间运营模式。
Company/Organization Profile
机构简介
Located adjacent to the scenic, culturally rich, and magically enchanting Wulongkou Ecological Wetland and the 4A-level Erlang Shen Ruins Theme Park, Daquan Experimental School in Guannan County covers an area of 64.5 mu. The school currently has 112 faculty members, 27 teaching classes, and 1,326 students. It is equipped with supporting physics, chemistry, and biology laboratories, as well as computer classrooms. Sports facilities include a track and field ground, basketball courts, and volleyball courts, while the library houses over 60,000 books.
In recent years, the school has promoted the "1+1 Independent Circular Ecological Classroom" model and actively advanced curriculum reform. It has successively won honors such as the "Excellent Achievement Award for Classroom Reform in Jiangsu Province", "Model School for Textbook Drama Creation in Jiangsu Province", "Lianyungang Scholarly Campus", "Characteristic School for Junior High School Teaching Team Construction in Lianyungang", and "Advanced Collective in Teaching and Research in Lianyungang". Adhering to the educational philosophy of "Ecological environment protection should start from an early age", the school deeply integrates the inheritance of red culture with green ecological education, constructing a distinctive quality education system with remarkable achievements particularly in ecological education. The Xiangyangyuan Labor Practice Base, built relying on the junior high school biology curriculum base, has become a green education brand integrating teaching, practice, and popular science.
灌南县大圈实验学校毗邻风光秀美、钟灵毓秀、梦幻神奇的五龙口生态湿地、4A景区二郎神遗迹主题公园。学校占地面积64.5亩,现有112名教职工,现有27个教学班,在校生1326人。有配套的理化生实验室和微机教室;拥有田径运动场、篮球场、排球场等,图书馆藏书有6万余册。近年来学校推进“1+1自主循环生态课堂”,积极推进课程改革,先后获得 “江苏省课堂改革优秀成果奖”、“江苏省课本剧创作示范学校”、“连云港市书香校园”、“连云港市初中教学团队建设特色学校”、“连云港市教科研先进集体”等荣誉称号,学校始终秉持 "生态环境保护从小从早抓起" 的教育理念,将红色文化传承与绿色生态教育深度融合。构建了特色鲜明的素质教育体系,尤其在生态教育领域成效突出,依托初中生物课程基地打造的向阳园劳动实践基地,成为集教学、实践、科普于一体的绿色教育品牌。

Project Outcome
项目成果
1.Reduction of Waste and Pollutants: Leveraging kitchen waste from the school cafeteria and organic waste from teachers and students, the base converts waste into natural fertilizer through composting technology, reducing annual waste removal by approximately 8 tons. It fully implements organic planting practices, with zero chemical pesticides used from seed selection to harvest, and chemical fertilizer usage reduced by over 60% compared to traditional planting. This not only avoids pesticide residue damage to soil microbial diversity but also lowers the risk of water eutrophication caused by fertilizer runoff, keeping soil heavy metal content within safety standards.
1. 废弃物与污染物减量:依托校园食堂厨余垃圾、师生生活有机废弃物,通过堆肥技术转化为天然肥料,年减少垃圾清运量约 8 吨;全面推行有机种植模式,从选种到收获零使用化学农药,化肥用量较传统种植减少 60% 以上,不仅避免了农药残留对土壤微生物多样性的破坏,还降低了化肥流失导致的水体富营养化风险,使基地土壤重金属含量维持在安全标准内。

2. Science Popularization and Participation Scale: The base organizes an average of 28 annual activities, including "World Environment Day Practice," "Parent-Child Organic Planting Classes," and "Ecological Monitoring Study Tours." Annual student participation reaches 1,200 person-times (covering 85% of the school’s junior high students), with over 400 visitors from surrounding communities and study groups from sister schools. Through the "Little Hands Pull Big Hands" campaign, it has inspired over 150 families to adopt habits of waste sorting, water conservation, and green protection, with the accuracy rate of family environmental behaviors increasing by 35% compared to pre-participation levels.
2. 科普与参与规模:年均开展 “世界环境日实践”“有机种植亲子课”“生态监测研学” 等活动 28 场次,其中学生年均参与 1200 人次(覆盖全校 85% 的初中生),接待周边社区居民、兄弟学校研学团体 400 余人次;通过 “小手拉大手” 行动,带动 150 余户家庭养成垃圾分类、节水护绿习惯,家庭环保行为正确率较参与前提升 35%。

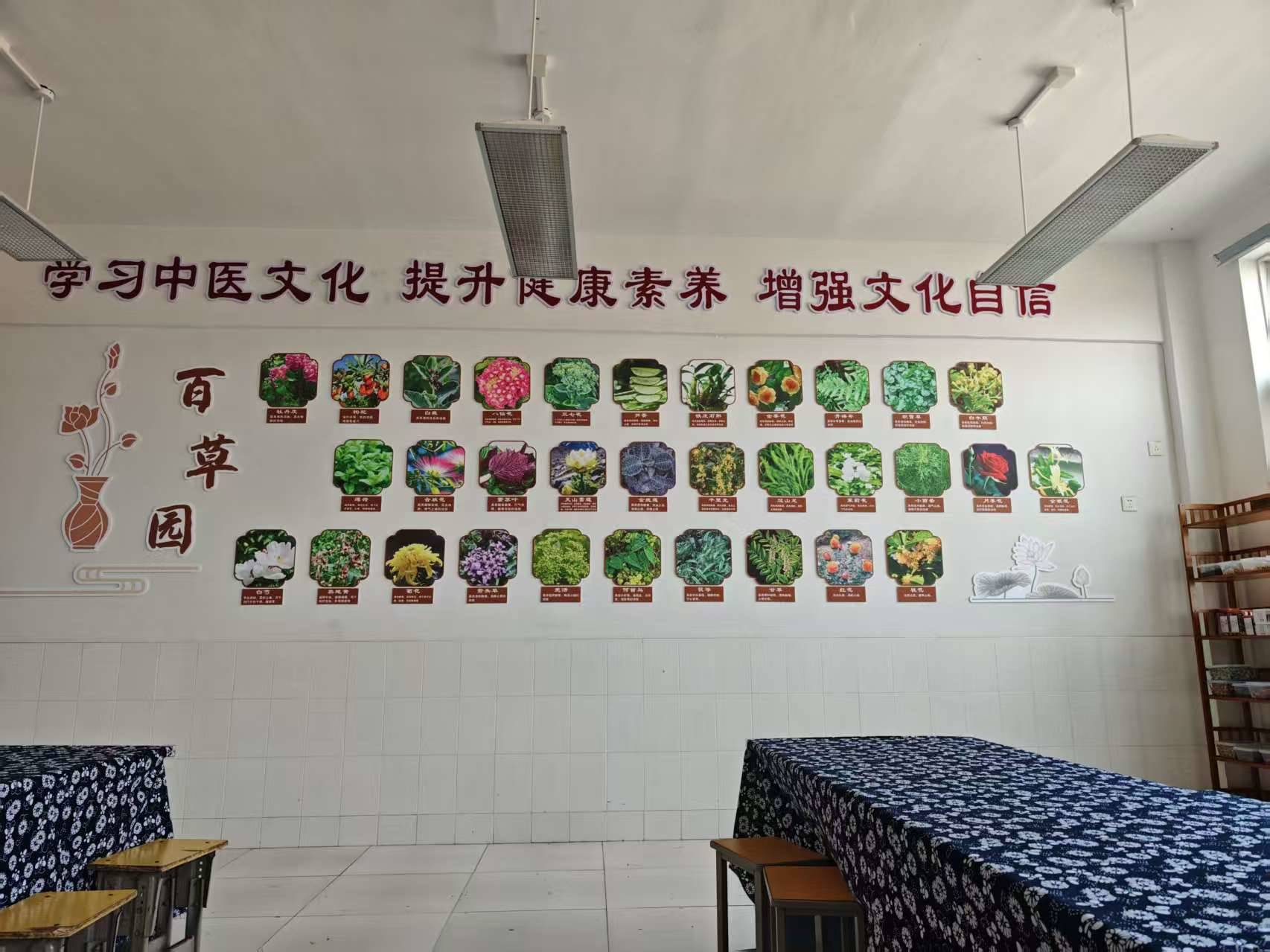
3. Ecological Environment Improvement: The base cultivates over 20 plant species, including local poplars, willows, roses, and medicinal plants like mint and dandelion, achieving over 90% vegetation coverage. Monitoring by the school’s weather station shows that in summer, the average temperature in the garden is 2-3℃ lower than in hardened campus areas, with air relative humidity increased by 15-20% and annual soil organic matter content rising by 0.2%. A micro-ecosystem has gradually formed, with 3 observed bird species (e.g., sparrows, turtledoves) and 5 beneficial insect species (e.g., ladybugs, bees), marking a significant enhancement in biodiversity.
3. 生态环境改善:基地种植本地杨、柳、月季及薄荷、蒲公英等药用植物共 20 余种,植被覆盖率超 90%;经校园气象站监测,夏季园内平均气温较校园硬化区域低 2-3℃,空气相对湿度提升 15-20%,土壤有机质含量年均提升 0.2%;逐步形成微型生态系统,已观测到麻雀、斑鸠等鸟类 3 种,瓢虫、蜜蜂等有益昆虫 5 种,生物多样性显著提升。

4. Social Benefits and Demonstration
Relevant practices have been reported 4 times by county-level media, including Guannan County TV Station and the "Guannan Education" official WeChat account. The school-based curriculum Exploration of Campus Green Spaces has become a compulsory practical course for 7th and 8th graders, with 20 annual class hours. The student-led monitoring model—recording air humidity and soil fertility data twice weekly to generate annual ecological reports—has been recognized. The school has received honors such as: Jiangsu Provincial Biology Curriculum Base
Jiangsu Provincial School for Primary and Secondary Students' Character Enhancement Project; Advanced Unit for Ecological Science Popularization Education in Jiangsu Province; Advanced Collective for Teaching and Research in Jiangsu Province; Lianyungang Characteristic School for Junior High School Teaching Team Construction; Lianyungang Green School. These achievements have enabled synergistic development in student iteracy improvement, teacher professional growth, and school brand enhancement. Three nearby schools have visited for exchanges, providing a replicable model for regional campus green space development.
4. 社会效益与示范:相关实践获灌南县电视台、“灌南教育” 公众号等县级媒体报道 4 次;开发的《校园绿色空间探究》校本课程,成为初一、初二年级必修实践课,年均开设 20 课时;“学生主导监测” 模式(每周 2 次记录空气湿度、土壤肥力数据,形成年度生态报告)获认可,学校先后获江苏省生物课程基地、江苏省中小学生品格提升工程项目学校、江苏省生态科普教育先进单位、江苏省教科研工作先进集体、连云港市初中教学团队建设特色学校、连云港市绿色学校、连云港市生态教育特色学校、连云港市新课程素养评价实验学校、连云港市优学乡村工程扩优示范学校、灌南县综合工作先进集体。实现学生素养提升、教师专业成长、学校品牌增值的协同发。周边 3 所学校前来交流学习,为区域校园绿色空间建设提供可落地的参考范式。

Project Highlights
项目亮点
The project centers on "ecological synergy + practical education", prioritizing the use of existing resources such as campus waste and rainwater, and innovating the model of "student-led monitoring + resource recycling + curriculum integration" to achieve synergy among planting, water conservation, and biology teaching. It has won the First Prize for County-level Campus Environmental Protection Practice and been reported by county-level media four times, with three schools visiting for exchange and learning. Teachers and students comment that "they can learn environmental protection through hands-on practice", and community residents praise it for driving families to develop green habits. Without additional policy preferential treatment, it has become a regional model.
项目以 “生态协同 + 实践育人” 为核心,优先用校园废弃物、雨水等既有资源,创新 “学生主导监测 + 资源循环 + 课程融合” 模式,实现种植、节水与生物教学协同。获县级校园环保实践一等奖,4 次县媒报道,3 所学校交流借鉴。师生评 “能动手学环保”,社区居民赞其带动家庭养成绿色习惯,无额外政策优惠却成区域示范。
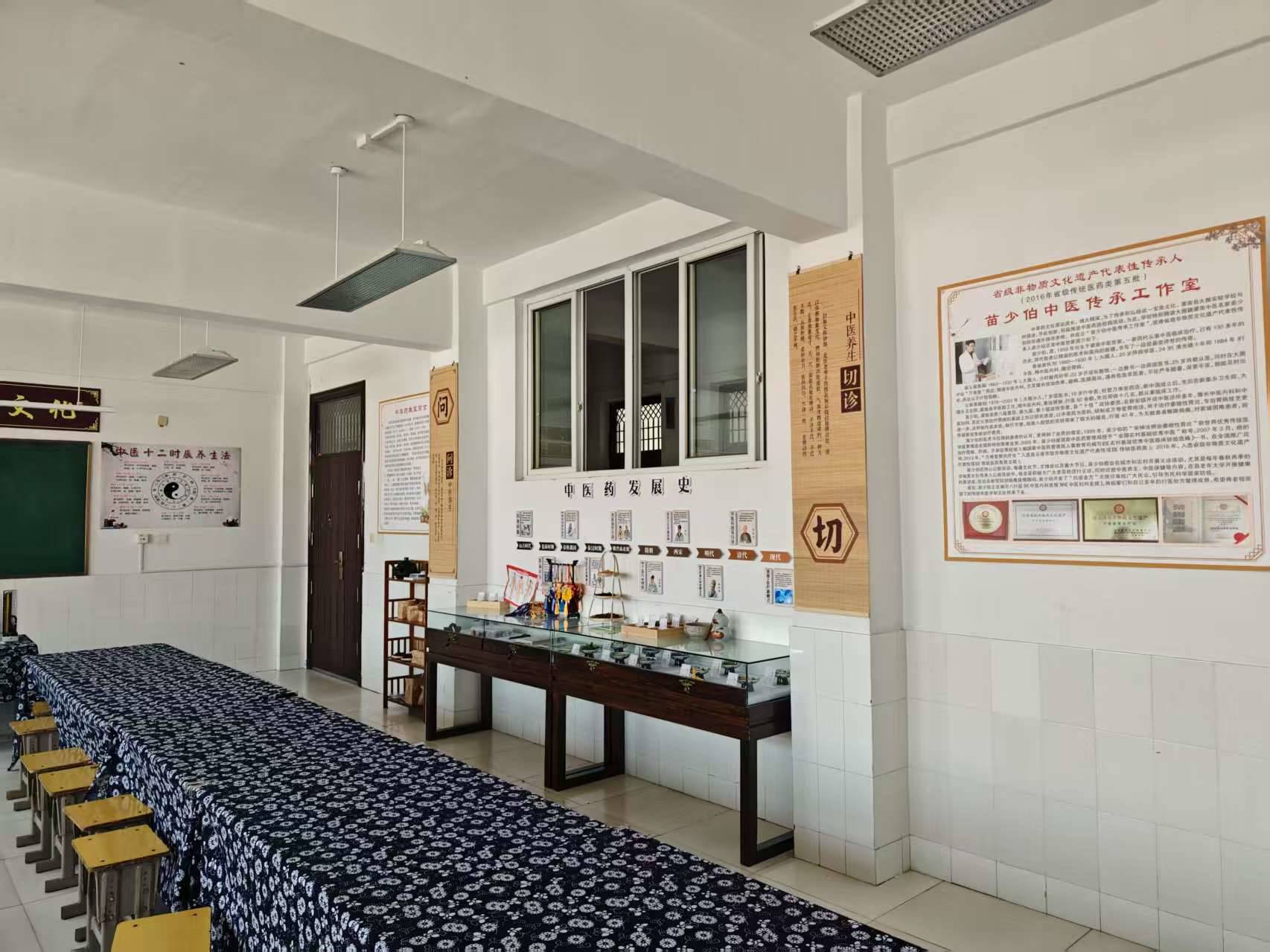

Project Implementation
项目实施
I. Implementation Plan and Process
The project will start preparation in January 2022 and will be promoted in three stages
Phase 1 (January 2022-March 2022): Planning and Design
Leveraging the school’s original idle land (unused area on the edge of the former playground), the project collaborated with experts from the County Bureau of Ecology and Environment and the Agricultural Technology Extension Center. Combined with the needs of biology courses, a construction plan featuring "native plants as the mainstay and clear functional zoning" was finalized. Core areas such as planting zones, observation zones, and composting zones were divided to avoid the occupation of additional land.
Phase 2 (April 2022-June 2022): Facility Construction
Teachers and students jointly participated in site leveling. A rainwater collection tank (with a capacity of 50m³) was built, drip irrigation pipelines were installed, and planting troughs were repurposed from used wooden crates. Organic composting equipment was purchased, and ecological interpretation signs were simultaneously produced to reduce construction costs.
Phase 3 (July 2022-Present): Operation Optimization
A three-level management mechanism of "principal-led, teacher-responsible, and student-grouped" was established. Two weekly biology practical classes are arranged to connect with base activities, facility maintenance is conducted monthly, and experts are invited for technical guidance each semester to continuously improve operational processes.
一、实施方案与过程
项目于 2022 年 1 月启动筹备,分三阶段推进:
第一阶段(2022.1-2022.3)为规划设计,依托学校原有闲置地块(原操场边缘未利用区域),联合县生态环境局、农业技术推广中心专家,结合生物课程需求,确定 “本土植物为主、功能分区明确” 的建设方案,划分种植区、观测区、堆肥区等核心区域,避免占用新增用地;
第二阶段(2022.4-2022.6)为设施建设,师生共同参与场地平整,搭建雨水收集池(容积 50m³)、安装滴灌管网,利用废旧木箱改造种植槽,采购有机堆肥设备,同步完成生态解说牌制作,降低建设成本;
第三阶段(2022.7 至今)为运营优化,建立 “校长牵头 - 教师负责 - 学生分组” 的三级管理机制,每周安排 2 节生物实践课对接基地活动,每月开展 1 次设施维护,每学期邀请专家进行技术指导,持续完善运营流程。

II. Comparison Before and After Implementation & Key Support
(I) Changes Before and After Implementation
Before implementation: The site was a barren wasteland with overgrown weeds, soil compaction, occasional garbage accumulation, and no ecological functions.
After implementation: Vegetation coverage increased from less than 10% to over 90%, forming a multi-layered "arbor-shrub-herb" vegetation structure. Additional ecological facilities such as rainwater recycling and composting systems were added, transforming the site into an integrated green space for teaching, ecology, and science popularization. Meanwhile, students’ ecological awareness shifted from "textbook theory" to "practical perception," and their enthusiasm for participating in environmental activities rose from an initial 40% to 90%.
(II) Overcoming Challenges and Support Guarantees
The project faced two key challenges: insufficient planting experience among teachers and students and limited operating funds. To address these:
Technical difficulties were resolved by inviting agricultural technology experts to conduct 4 sessions of planting training and establishing "student technical teams" for mutual learning and support.
Funding was secured through a combination of school public funds (60%) and special allocations from the County Education Bureau (40%), ensuring facility maintenance and activity implementation.
In terms of support:
Internally: The Academic Affairs Office coordinated curriculum integration, while the General Affairs Office was responsible for facility operation and maintenance.
Externally: The County Bureau of Ecology and Environment provided environmental publicity materials, the County Committee for the Care of the Next Generation awarded the title of "Off-Campus Labor Education Base," and surrounding communities assisted in promoting open-day activities. This formed an "internal-external linkage" support system.
二、实施前后对比与关键支撑
(一)实施前后变化
实施前,场地为裸露荒地,存在杂草丛生、土壤板结问题,偶有垃圾堆积,无生态功能;实施后,植被覆盖率从不足 10% 提升至 90% 以上,形成 “乔灌草” 多层植被结构,新增雨水循环、堆肥等生态设施,成为集教学、生态、科普于一体的绿色空间。同时,学生生态认知从 “课本理论” 转向 “实践感知”,参与环保活动的积极性从初期的 40% 提升至 90%。
(二)挑战克服与支持保障
项目曾面临 “师生种植经验不足”“运营资金有限” 两大挑战:通过邀请农技专家开展 4 期种植培训、组建 “学生技术小组” 互帮互学,解决技术难题;依托学校公用经费(占比 60%)+ 县教育局专项拨款(占比 40%),保障设施维护与活动开展。支持方面,内部有学校教务处统筹课程对接、总务处负责设施运维;外部获县生态环境局提供的环保宣传材料、县关工委授予 “校外劳动教育基地” 称号,周边社区协助
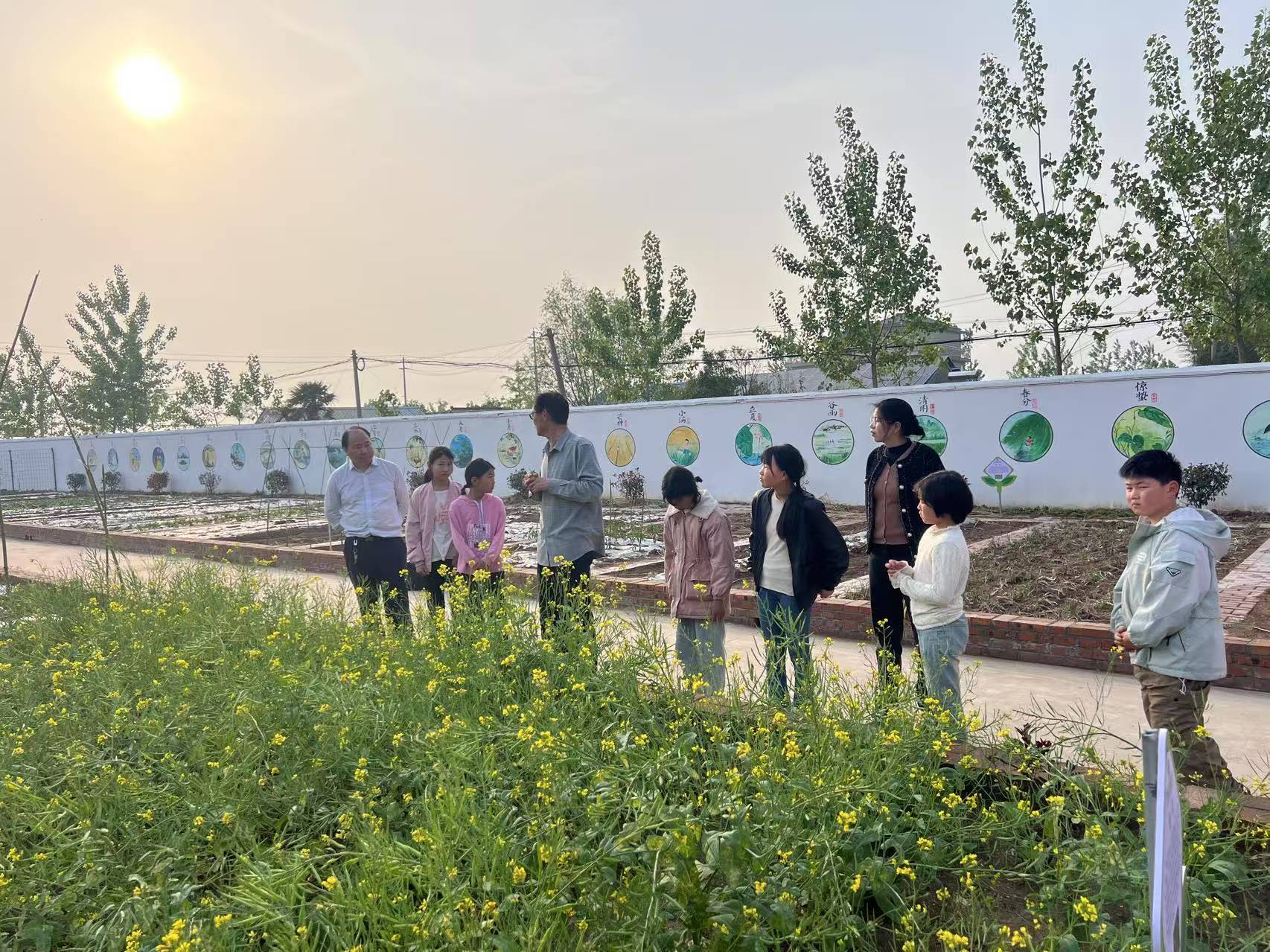

Project Impact & Sustainability
项目影响力、可推广性与可持续性
The project features both technological and institutional innovations: Technologically, it has implemented low-cost models such as rainwater collection and recycling irrigation, and kitchen waste composting without the need for complex equipment. Institutionally, it pioneered a three-level management system of "school-led, teacher-responsible, and student-monitored", established student ecological observer teams, and formed an operation system co-maintained by teachers and students.
In terms of influence, it has promoted ecological education from classroom to practice. The developed school-based curriculum has been included in regional teaching and research cases, inspiring 3 surrounding schools to carry out similar construction. School-community collaborative activities have enhanced community environmental awareness, and the project has been recommended by the county ecological environment bureau as a "Campus Environmental Protection Practice Demonstration Site".
项目兼具技术与机制创新:技术上,低成本落地雨水收集 - 循环灌溉、厨余堆肥等模式,无需复杂设备;机制上,首创 “学校主导 + 教师负责 + 学生监测” 三级管理,组建学生生态观察员队伍,形成师生共护的运营体系。
影响力方面,推动生态教育从课堂走向实践,开发的校本课程被纳入区域教研案例,带动周边 3 所学校开展类似建设;校社联动活动让社区环保意识提升,获县生态环境局推荐为 “校园环保实践示范点”。

It boasts strong replicability. Relying on idle campus space, the project features low construction and operation costs. The supporting Green Space Management Manual and Practical Activity Guide can be directly referenced by rural primary and secondary schools without the need for additional large-scale investment.
Sustainability is ensured: Future plans include upgrading the intelligent irrigation system, deepening cooperation with the county agricultural technology station to introduce native plant cultivation technology, and conducting "Green Mentor" training to cultivate on-campus ecological education backbones, ensuring long-term project operation and sustained environmental education impact.
可推广性强,项目依托校园闲置空间,建设运维成本低,配套的《绿色空间管理手册》《实践活动指南》可直接供乡镇中小学参考,无需额外投入大量资金。
可持续性有保障:后续计划升级智能灌溉系统,深化与县农技站合作引入本土植物培育技术;同时开展 “绿色导师” 培训,培养校内生态教育骨干,确保项目长期运营并持续发挥环保育人作用。
(Using AI translation)
(使用AI翻译)

零废弃学校建设之厨余垃圾篇
10-24 · 来源:中国浙江省宁波市鄞州第二实验中学 · 作者:中国浙江省宁波市鄞州第二实验中学

能源至净,生活至美,积极打造碳中和
10-24 · 来源:中国石化销售股份有限公司海南海口石油分公司 · 作者:中国石化销售股份有限公司海南海口石油分公司
无锡中瑞低碳生态城
10-23 · 来源:无锡中瑞低碳生态城 · 作者:无锡中瑞低碳生态城